Knowledge
-
- May 05, 2025
Optical fibers are commonly used for data transmission in industrial environments, particularly when cable runs exceed 100 meters and copper Ethernet is no longer viable. The general assumption is simple: once installed, the cable does its job – transmitting data from point A to B – and that's it. There is a common opinion that there are no special requirements for data transmission via fiber optics. Especially in hazardous areas, this assumption is not only persistent but is potentially dangerous.
The common belief is that optical wave guides (OWGs) are inherently safe because they transmit light rather than electrical current. As such, they are frequently installed without additional precautions, under the impression that they pose no ignition risk. System operators often express surprise when questioned about safety standards for fibre optics in hazardous environments, pointing out that such systems have been operating for years without incident.
However, this is actually a big misconception!
-
- April 23, 2025
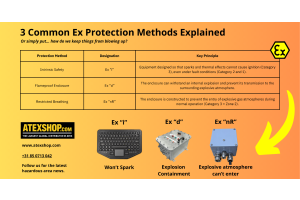
Explosion protection methods are essential to ensuring equipment can safely operate in hazardous areas where flammable gases, vapours, or mists may be present. Among the most recognized methods are Ex d (flameproof), Ex e (increased safety), and Ex i (intrinsic safety). But what about Ex nR?
Defined in the standard EN IEC 60079-15, Ex nR—or the restricted-breathing enclosure—is a lesser-known explosion protection method for equipment used in Zone 2 hazardous areas. This method focuses on preventing the ingress of explosive atmospheres into the enclosure, reducing the risk of ignition during normal operation.
Let’s dive into what makes Ex nR unique, what types of devices typically use it, and how the relevant standard (60079-15) outlines its implementation.